R&D Projects

Fault Management Framework for FPGA-Based Satellite Electronics
The ESA-funded GSTP project SoC-HEALTH2 expanded the OCFM framework, which was developed in a precursor project SoC-HEALTH, to extend support for advanced FPGA SoC platforms like AMD/Xilinx Versal ACAP (Adaptive Compute Acceleration Platform) .
The increasing complexity and mission-critical nature of satellite electronics require advanced fault management solutions to ensure long-term reliability, fault tolerance, and operational continuity in harsh space environments. The proposed development plan integrates the On-Chip Fault Management (OCFM) framework into Xilinx Versal ACAP, an advanced and heterogeneous platform well-suited for satellite applications. This comprehensive plan addresses the unique challenges posed by radiation, thermal variations, and system failures in space.
Core Objectives
The primary goal of this initiative is to develop and implement a robust, scalable fault management framework tailored to satellite systems using the Versal ACAP platform. The solution leverages OCFM’s real-time fault detection, isolation, and recovery capabilities, ensuring minimal downtime and optimized resource utilization even under adverse conditions.
Key Components of the Development Plan
Embedding fault monitors and sensors across Versal ACAP's heterogeneous architecture, including AI engines, programmable logic, and NoC (Network-on-Chip).
Implementing Reconfigurable Scan Networks (RSN) for fault management in compliance with IEEE 1687 standards.
Centralizing fault data aggregation and reporting through the Instrument Manager (IM) and Health Map (HM).
Value Proposition
The development plan brings a transformative approach to satellite fault management by combining Versal ACAP’s advanced features with the modular and extensible design of OCFM. Key benefits include:
Reliability: Real-time fault management significantly enhances system resilience, reducing risks of mission-critical failures.
Cost Efficiency: Reduced reliance on hardware redundancy decreases satellite payload weight and launch costs while increasing usable system capacity.
Future Readiness: The use of AI models and modular APIs ensures adaptability for future mission needs and evolving space requirements.
Sustainability: Fault prediction and graceful degradation mechanisms extend mission lifespans, improving the return on investment.
Strategic Importance By addressing key pain points such as radiation-induced faults, limited system redundancy, and scalability challenges, this initiative aligns closely with the needs of satellite operators seeking to enhance mission success rates and minimize operational risks. The integration of OCFM with Versal ACAP establishes a cutting-edge solution for the next generation of space electronics.
This development plan leverages earlier developed OCFM framework’s advanced fault management capabilities to deliver unparalleled reliability and resilience for Versal ACAP-based satellite electronics. The proposed solution not only addresses current challenges but also positions satellite systems for long-term success in increasingly demanding space missions.
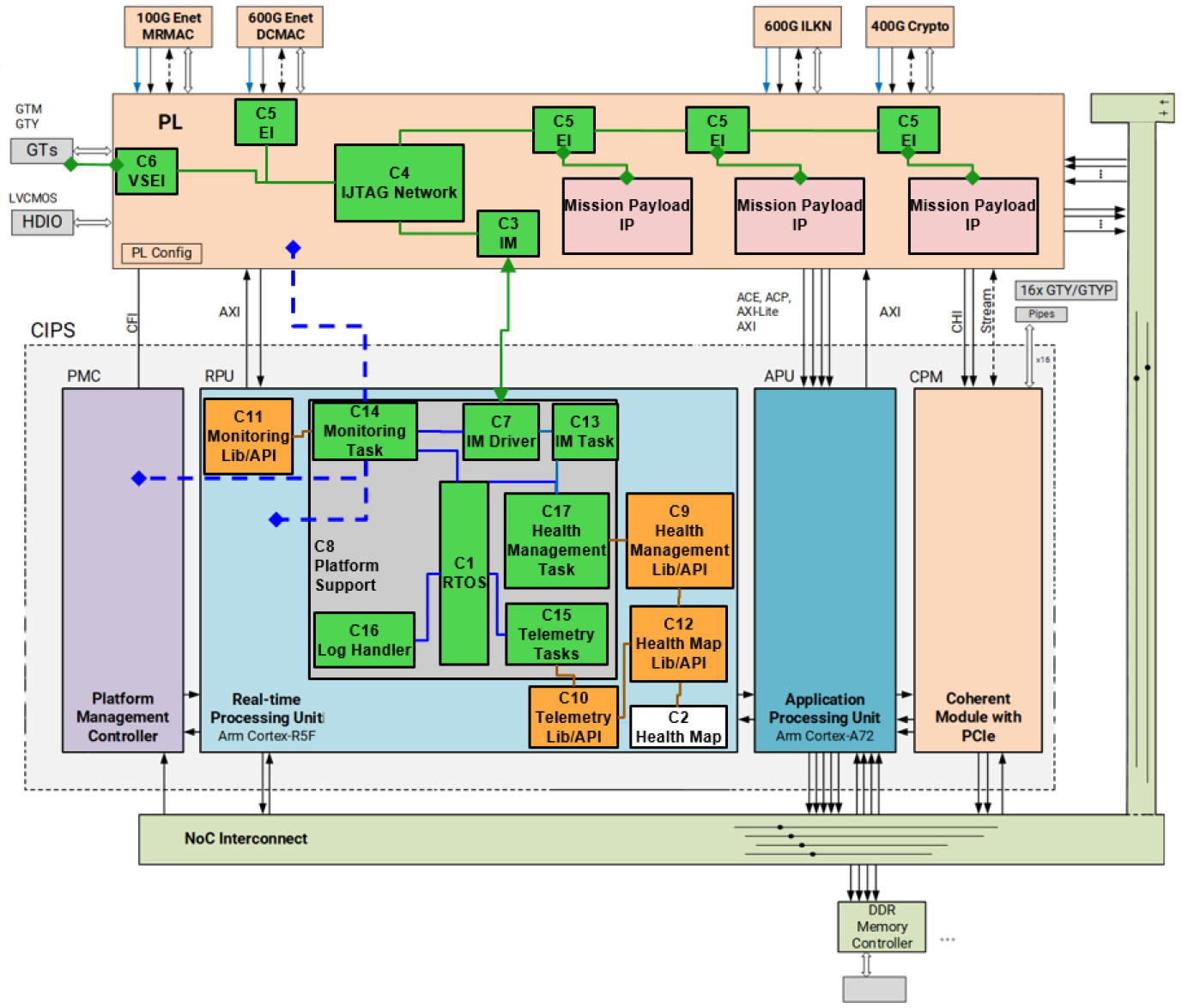
Health management demo components location in Xilinx Versal ACAP platform
Project Fact Sheet
- Budget: 200 kEUR
- Duration: 2023 - 2025
- Partners: European Space Agency ESTEC (end user), Testonica Lab (contractor)
- Contract Number: GSTP Element 1 activity No 4000139825/22/NL/AS
- Final Report download: soc-health2-FR.pdf

On-chip health monitoring and fault management for SoC health-awarness in Space Missions — SoC-HEALTH
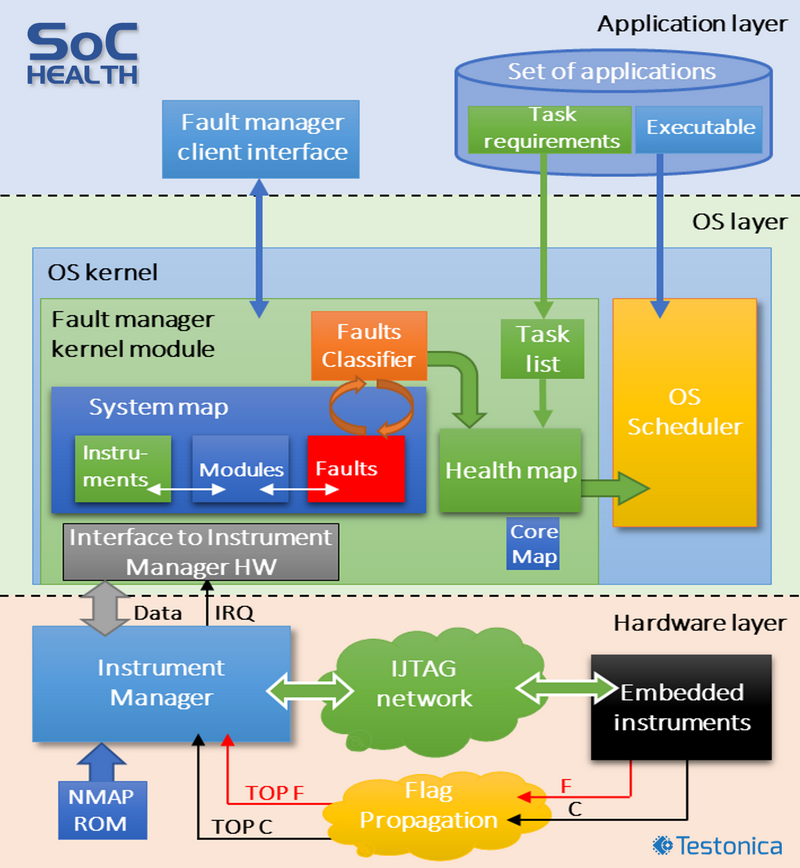
Due to harsh space environments, especially at GEO orbits populated by telecom satellites, the non-hardened microelectronics would suffer from transients and soft errors. Although, the space electronics is normally hardened and equipped with fault tolerance and soft error mitigation schemes, the radiation damage and wear out accumulating over time would eventually lead to non-tolerable permanent defects that render the target application dead. In fact, the presence of permanent defects doesn’t necessarily mean the end of life if the electronic system is aware of its health status and thereby can cope with the reduced processing capacity. The technology trend observed today in microelectronics leads to system resilience that in addition to physical hardening and classical fault tolerance , would also exploit the extensive natural redundancy of multi-core systems together with a smarter task scheduling.
In SoC-HEALTH project, Testonica is to develop a demonstrator of a fine-grain in-situ On-Chip Fault Management (OCFM) that acts as the backbone of SoC (system on chip) Health-Awareness. The SoC Health Awareness conception relies on the reuse of multitude of typical sensors and checkers already embedded deep into the hardware to measure operating parameters of the target IP core, detect and correct errors before they manifest at the application software level. The conception also includes on-chip health monitoring of the hardware, maintains SoC health map, and supports adaptation of the OS and the software to the reduced capacity of SoC sub-modules and sub-systems keeping the mission alive until the electronics is completely dead.
The new Health Awareness technology is expected to rapidly expand frontiers for real-life applications in 5-10 years. The SoC-HEALTH technology acts as a middleware between HW checkers/sensors and mission applications, thus providing Health Awareness functions for next generation multi-core processors in space industry but also in terrestrial economy, especially in the domains requiring high availability of the electronics.
The degradation monitoring as well as fault detection may take place at different system levels: the hardware (HW) and software (SW). Still, the key to a successful OCFM is the ability to simultaneously collect and process data from dozens or even hundreds of on-chip sensors and checkers in real time independent of the system size and configuration, which is not a trivial task.
The key target of the project is building on Kintex7 FPGA a demonstration platform based on octa-core LEON3 CPU augmented with OCFM facilities as well as enhancement of Linux OS/kernel with fault management functionality. With that, Testonica aims at demonstrating that monitoring, diagnostic and fault management functions based on underlying IEEE 1687 infrastructure and instrumentation can both deliver high-performance fault management as well as create a reasonable overhead impact on the underlying system performance and cost.
Project Fact Sheet
- Budget: 200 kEUR
- Duration: August 2018 - February 2020
- Partners: European Space Agency ESTEC (end user), Testonica Lab (contractor)
- Contract Number: Incentive Scheme / EXPRO+ and GSTP activity 4000124897/18/NL/CBi
- Final Report download: 4000124897_SoC_HEALTH_FR.pdf

ELIKO Competence Centre project
ELIKO launched an Internet of Things (IoT) driven industrial R&D program in 2015. The aim of the project to help companies develop competitive products through active collaboration with universities. This is to ensure that companies invest in future-proof technologies in the IoT. The program has two focus areas. Projects under the first area, sensing and signal processing in the IoT, develop algorithms suitable for compact and energy efficient electronic devices. Better energy efficiency is essential for future connected applications. In the second focus area, Eliko designs software and communication solutions that simplify data transmission in the IoT environment. IoT infrastructures, applications and services combine complex set of technologies to deliver end-user applications for smart cities, smart factories and the smart home. The program includes 22 industry-led R&D projects in a range of fields.
In the project, Testonica is focusing on development of advanced test systems of further IoT devices. Due to high-speed nature and complexity of modern embedded systems, the traditional means of testing (e.g. with the help of external test and measurement equipment) often become inefficient. Our task is to develop FPGA-based smart embedded instruments, i.e. ready-made firmware components/IP cores that are injected into programmable components of IoT devices for test purposes.
Project Fact Sheet
- Budget: 7 MEUR
- Duration: July 2015 - June 2022
- Partners: Artec Design, ASAN Security Technologies, Cybernetica, Degeetia, Elvior, FlyDog Marine, GoSwift, Haapsalu Neurological Rehabilitation Centre, Injeq, ITT Group, Martem, Norcar Group, North Estonia Medical Centre, Positium, Protobios, Reach-U, Ridango, Safetoact, Selfdiagnostics, Sirius Microwave, Telegrupp, Testonica Lab, Threod Systems, West Tallinn Central Hospital
- Contract Number: EU48693
- Project page: http://www.eliko.ee/competence-centre-program/


Integrated Modelling, Fault Management, Verification and Reliable Design Environment for Cyber-Physical Systems (IMMORTAL)
In European Union's Horizon 2020 Research & Innovation Action IMMORTAL (Integrated Modelling, Fault Management, Verification and Reliable Design Environment for Cyber-Physical Systems) a consortium of leading European academic and industrial players aim at combining their expertise in developing an integrated, cross-layer modeling based tool framework for fault management, verification and reliable design of dependable Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS).
Recently, the world has seen emerging Cyber-Physical System (CPS) modelling frameworks addressing various design aspects such as control, security, verification and validation. However, there have been no considerations for reliability and automated debug (i.e. design error localisation and correction) aspects. The main aim of IMMORTAL is to fill this gap by introducing reliable design and automated system debug into CPS modelling. To reach this aim, the project will develop a cross-layer CPS model spanning analogue mixed-signal circuits, hardware architecture, firmware, operating system and application layers. In addition, a holistic fault model for representing fundamentally different error sources in CPSs (design bugs, wear-out and environmental effects) in a uniform manner will be proposed. Moreover, IMMORTAL plans to develop a fault management infrastructure on top of the reliable design framework that would allow ultra-fast fault detection, isolation and recovery in the emerging many-core based CPS architectures that are expected to be increasingly adopted in the coming years.
As a result, the project will enable the development of dependable CPSs with improved reliability and extended effective life-time, which is a particular concern in emerging nanoelectronics technologies that are becoming increasingly vulnerable to disturbances, ageing and process variations. The tool framework to be developed within IMMORTAL will be evaluated on a clearly specified real-world use-case of a satellite on-board-computer. However, since the results are more general and applicable to many application domains, including avionics, automotive and telecommunication, demonstration of the framework tools will be applied to CPS examples from other domains as well.
Project Fact Sheet
- Budget: 4 MEUR
- Duration: March, 2015 – February, 2018
- Partners: Tallinn University of Technology (Estonia), German Aerospace Center (DLR) (Germany), Graz University of Technology (Austria), University of Twente (Netherlands), IBM (Israel), Testonica Lab, Recore Systems (Netherlands)
- Contract Number: 644905 - IMMORTAL - H2020-ICT-2014
- Project page: http://h2020-immortal.eu

Board and SoC Test Instrumentation for Ageing and No Failure Found (BASTION)
Today, an average family spends over 50 Euros of hidden costs annually on No-Failure-Found (NFF) investigations - a known problem of an unknown origin. Tomorrow, the electronic engine control system in a car will be dying after three-five years of operation due to CMOS aging. Actions are urgently needed!
In January 2014, work commenced on a European Union's 7th Framework Programme's collaborative research project FP7-ICT-2013-11-619871 BASTION (www.fp7-bastion.eu) BASTION - Board and SoC Test Instrumentation for Ageing and No Failure Found.
A group of European experts will unite their forces in BASTION to fight against aging and bring an NFF relief to the society. We will step into dark waters of unknown defects, uncertain fault coverage, unclassified field returns. We will build a new defect universe and string the faults into comprehensive classes. We will deeply study the mechanisms of ageing and reduce the semiconductor "wrinkles". A "magic wand" of embedded instrumentation and respective IEEE 1687 standard will help us to get under the hood and into the mechanics, build-up an ultra fast scalable error detection and localization infrastructure as well as integrate all heterogeneous methodologies and techniques into a homogeneous system.
BASTION brings together eight partners. Infineon (Germany), as the largest chip supplier to the automotive industry together with two high-tech SMEs, Aster Technologies (France) and Testonica Lab (Estonia), and five European universities: Politecnico di Torino (Italy), Universities of Twente (The Netherlands) and Lund (Sweden), Tallinn University of Technology (Estonia) and High School Hamm-Lippstadt (Germany) form the BASTION consortium being coordinated by Dr. Artur Jutman from Testonica Lab.
The project will complete in three years, at only a negligible fraction of costs wasted by society on NFF annually.
Project Fact Sheet
- Budget: 4.65 MEUR
- Duration: January, 2014 – March, 2017
- Partners: Testonica Lab (coordinator), Aster Technologies (France), Lund University (Sweden), Politecnico di Torino (Italy), Tallinn University of Technology (Estonia), High School Hamm-Lippstadt (Germany), Infineon Technologies (Germany)
- Contract Number: 619871 - BASTION - FP7-ICT-2013-11
- Project page: http://fp7-bastion.eu